Ukraine: the fate of displaced persons
War in the Ukraine has caused about 1,5 million internally displaced persons. The living conditions of those who have fled the war zone in the east of the country are often very difficult. Report
(This text is published as a collaboration between OBC and Eurozine, part of the Eurozine-project ‘Beyond conflict stories: Revealing public debate in Ukraine ’ supported by a grant from the Open Society Initiative in Europe within the Open Society Foundations)
When military planes flashed through the spring sky of Luhansk three years ago, and shots were heard in some areas of the city, Elena Dyurugyna, 34, knew that things would only get worse. She was right. Luhansk, Donetsk and the insurgent areas in eastern Ukraine would shortly become the theatre of a war between government forces and pro-Russian rebels.
At the time, Elena’s daughter was two years old. “I thought she should not see the war. I had work to finish. As soon as I was done I went to Kiev. I had no other choice. I had studied in the capital for two years, so I knew it and liked it. My husband had to stay in Luhansk during the worst of the fighting because of his work. Then, in September of 2014, he joined us”.
Elena is a photographer, and when she left Luhansk she sold her camera and her equipment. She needed money for the travel, to pay the rent and to feed her daughter. At the beginning, in Kiev, she worked in a MacDonald’s. She didn’t think she would return to her old job, at least not soon. However, she did go back to taking photos. She specialised in photos of children, and has kindergartens and schools among her clients. She takes portraits and she does weddings. Her studio is on the eleventh floor of a building near the Livoberezhna underground station. It is the same address as the head office of the NGO, Krymskaya Diaspora, that originally started to help those fleeing Crimea, the southern peninsula annexed to Russia in March of 2014. They quickly widened their action to help displaced persons from the crisis in Donbass, which followed closely on that of Crimea.
NGOs and Internally Displaced Persons
While attending a business course at Krymskaya Diaspora, Elena Dyurugyna was given the money necessary to buy back a camera and the necessary equipment. Krymskaya Diaspora made a studio available to her. “The course was useful. It taught me how to plan, to develop a strategy and how to promote myself. It was also very competitive. We were two hundred and only seventeen of us received funds”.
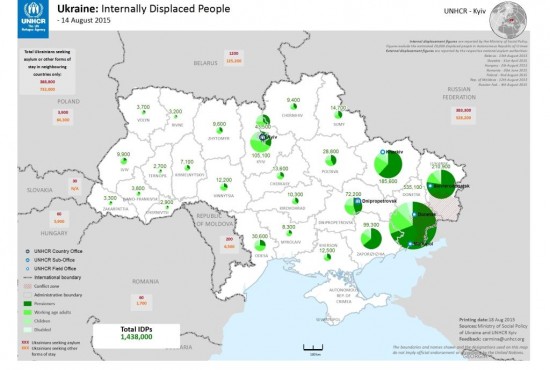
Krymskaya Diaspora is only one of the NGOs, almost all of which are organised by volunteers and obliged to work with donations, helping in Kiev and in the rest of the country those internationally known as Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs). That is, those who have left their homes and moved to other cities and places in Ukraine because of the conflict. According to the latest data relating to August 2015 from the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), the number of IDPs in Ukraine is around 1,5 million. Another one million have gone to Russia, according to the authorities in Moscow.
Even the choice of where to go is politically motivated. This could not be otherwise in a country which has been brutally divided since the Maidan uprising. Those who cross the border feel an empathy for Russia, and do not trust the government in Kiev. “Those who leave the area under the control of the latter, make an informed choice for Ukraine, whereas crossing into Russia would be easier”, says Lesia Lytvynova, co-founder of Frolivska 9/11, another NGO helping displaced persons.
Their life is not easy. “About two years ago, the government passed a law to protect their social rights and to initially allow them a financial contribution”, states Olga Semenova, from the Job Centre for free people, another NGO helping the IDPs. “However, this is bound by technical and bureaucratic steps which, in reality, make it difficult to function. These people are asked to produce documentation, which mostly they do not have. Therefore, our task is to defend their rights to health services, to work, to kindergarten and to study”.
Resettlement in Kiev
Employment is the main theme of the organisation for which Olga Semenova works, as indicated by the name. “Of the more than 15,000 people who contacted our NGO in our first two years of activity, a third have found work. We have 3,000 companies listed in our database. We have also organised professional courses for 5,500 people and allowed fifty startups to get going”.
To act as a bridge between displaced people and companies is in itself hard work. Even more so in a situation such as this, marked by a deep depression. In 2015, the country lost 9,9 GDP points. Also "many of the displaced persons are miserable, frustrated. Out of ten who turn to us, an average of only three are motivated”, Natalia tells us. She works at the Job Centre for free people answering the calls coming in on the specially created number.
Frustration feeds on the scarcity of work opportunities, and on a sense of disorientation, having had to leave one’s own land. Resettlement in Kiev is not always easy. “At the beginning, local people were supportive towards these people arriving without anything. They were willing to give, sometimes even to give hospitality. But as time passed things gradually changed. The state did not take all the responsibility it should have taken. The management of the displaced persons fell on the local communities”, says Lesia Lytvynova.
The Frolivska 9/11 storeroom is connected to the road by a window. Anyone who wants can leave food, clothing and toys. A couple in their sixties passes. They have a sack with them from which they take out something for the refugees. They still give.
Featured articles
- Take part in the survey
Ukraine: the fate of displaced persons
War in the Ukraine has caused about 1,5 million internally displaced persons. The living conditions of those who have fled the war zone in the east of the country are often very difficult. Report
(This text is published as a collaboration between OBC and Eurozine, part of the Eurozine-project ‘Beyond conflict stories: Revealing public debate in Ukraine ’ supported by a grant from the Open Society Initiative in Europe within the Open Society Foundations)
When military planes flashed through the spring sky of Luhansk three years ago, and shots were heard in some areas of the city, Elena Dyurugyna, 34, knew that things would only get worse. She was right. Luhansk, Donetsk and the insurgent areas in eastern Ukraine would shortly become the theatre of a war between government forces and pro-Russian rebels.
At the time, Elena’s daughter was two years old. “I thought she should not see the war. I had work to finish. As soon as I was done I went to Kiev. I had no other choice. I had studied in the capital for two years, so I knew it and liked it. My husband had to stay in Luhansk during the worst of the fighting because of his work. Then, in September of 2014, he joined us”.
Elena is a photographer, and when she left Luhansk she sold her camera and her equipment. She needed money for the travel, to pay the rent and to feed her daughter. At the beginning, in Kiev, she worked in a MacDonald’s. She didn’t think she would return to her old job, at least not soon. However, she did go back to taking photos. She specialised in photos of children, and has kindergartens and schools among her clients. She takes portraits and she does weddings. Her studio is on the eleventh floor of a building near the Livoberezhna underground station. It is the same address as the head office of the NGO, Krymskaya Diaspora, that originally started to help those fleeing Crimea, the southern peninsula annexed to Russia in March of 2014. They quickly widened their action to help displaced persons from the crisis in Donbass, which followed closely on that of Crimea.
NGOs and Internally Displaced Persons
While attending a business course at Krymskaya Diaspora, Elena Dyurugyna was given the money necessary to buy back a camera and the necessary equipment. Krymskaya Diaspora made a studio available to her. “The course was useful. It taught me how to plan, to develop a strategy and how to promote myself. It was also very competitive. We were two hundred and only seventeen of us received funds”.
Krymskaya Diaspora is only one of the NGOs, almost all of which are organised by volunteers and obliged to work with donations, helping in Kiev and in the rest of the country those internationally known as Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs). That is, those who have left their homes and moved to other cities and places in Ukraine because of the conflict. According to the latest data relating to August 2015 from the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), the number of IDPs in Ukraine is around 1,5 million. Another one million have gone to Russia, according to the authorities in Moscow.
Even the choice of where to go is politically motivated. This could not be otherwise in a country which has been brutally divided since the Maidan uprising. Those who cross the border feel an empathy for Russia, and do not trust the government in Kiev. “Those who leave the area under the control of the latter, make an informed choice for Ukraine, whereas crossing into Russia would be easier”, says Lesia Lytvynova, co-founder of Frolivska 9/11, another NGO helping displaced persons.
Their life is not easy. “About two years ago, the government passed a law to protect their social rights and to initially allow them a financial contribution”, states Olga Semenova, from the Job Centre for free people, another NGO helping the IDPs. “However, this is bound by technical and bureaucratic steps which, in reality, make it difficult to function. These people are asked to produce documentation, which mostly they do not have. Therefore, our task is to defend their rights to health services, to work, to kindergarten and to study”.
Resettlement in Kiev
Employment is the main theme of the organisation for which Olga Semenova works, as indicated by the name. “Of the more than 15,000 people who contacted our NGO in our first two years of activity, a third have found work. We have 3,000 companies listed in our database. We have also organised professional courses for 5,500 people and allowed fifty startups to get going”.
To act as a bridge between displaced people and companies is in itself hard work. Even more so in a situation such as this, marked by a deep depression. In 2015, the country lost 9,9 GDP points. Also "many of the displaced persons are miserable, frustrated. Out of ten who turn to us, an average of only three are motivated”, Natalia tells us. She works at the Job Centre for free people answering the calls coming in on the specially created number.
Frustration feeds on the scarcity of work opportunities, and on a sense of disorientation, having had to leave one’s own land. Resettlement in Kiev is not always easy. “At the beginning, local people were supportive towards these people arriving without anything. They were willing to give, sometimes even to give hospitality. But as time passed things gradually changed. The state did not take all the responsibility it should have taken. The management of the displaced persons fell on the local communities”, says Lesia Lytvynova.
The Frolivska 9/11 storeroom is connected to the road by a window. Anyone who wants can leave food, clothing and toys. A couple in their sixties passes. They have a sack with them from which they take out something for the refugees. They still give.