
Foto Unsplash - Daniel Mensah Boafo
The latest ILO report shows that migrant workers have more precarious contracts and earn 13 percent less on average than domestic workers, for equal work. This gap is widening, and is particularly stark for female migrants
In many high-income countries migrant workers, women and men, make up a significant portion of the workforce and make an important contribution to society and the economy. However, for equal work, they earn almost 13 percent less than domestic workers, and this gap is only widening.
The data comes from the International Labour Organisation report, The migrant pay gap: understanding wage differences between migrants and nationals , published in December 2020 and covering 49 countries.
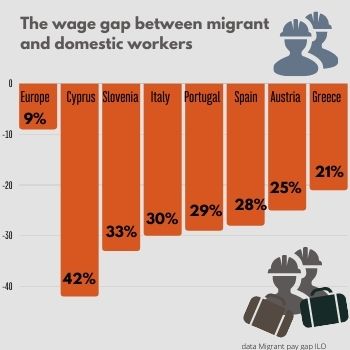
According to the data, in some countries the wage gap was especially high in 2019. For example, in Cyprus migrants earned 42 percent less than national workers, in Italy they earned 30 percent less, and in Greece migrants earned 21 percent less. The EU average is much lower – around nine percent.
Part of this wage gap remains "unexplained", that is, not due to the characteristics of the national labor market or the skills of the worker: it could, instead, be traced back to discrimination against foreign workers.
Compared to domestic workers, migrant workers earn less even when they possess similar qualifications within the same occupational category. Moreover, in high-income countries migrant workers with higher levels of education are less likely to obtain higher-skilled jobs. Job insecurity is also all too common. 27 percent of migrant workers have fixed-term contracts, and 15 percent have part-time contracts. Migrants are mostly employed in the primary sector (agriculture or fishing, for example), while in the secondary sector they have jobs in mining, manufacturing and construction.
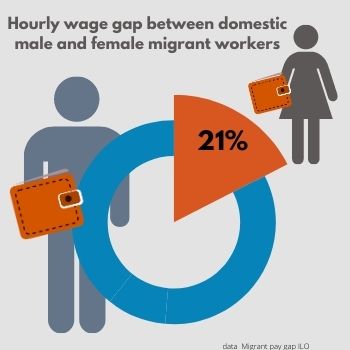
Gender also plays a significant role here. Female migrant workers suffer double wage discrimination, earning on average less than both domestic workers and male migrants. In high-income countries, the hourly wage gap between domestic male and female migrant workers is estimated at nearly 21 percent. This is higher than the 16 percent gender pay gap in these countries.
Presenting the report, Michelle Leighton, head of the ILO’s Labor Migration branch, said that "tackling discrimination and prejudice that are deeply entrenched in the workplace and our society is more important than ever. Addressing the migrant pay gap is not only a matter of social justice, but will reduce inequalities between men and women and overall poverty."








 To Top
To Top